Selecting the Right Antenna for Your LoRaWAN® Gateway: A Comprehensive Guide
Choosing the right antenna for your LoRaWAN gateway is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring reliable connectivity. With various options available, it’s important to understand the specifications and factors that influence antenna selection. This guide aims to provide you with the essential information needed to make an informed decision.
Understanding Antenna Specifications
- IP Ratings: When selecting an antenna, it’s important to consider its IP rating, which indicates its resistance to dust and water. Two common ratings are:
- IP67: Offers complete protection against dust and can withstand immersion in water up to 1 meter deep for 30 minutes.
- IP65: Provides complete protection against dust and can resist water jets from any direction.
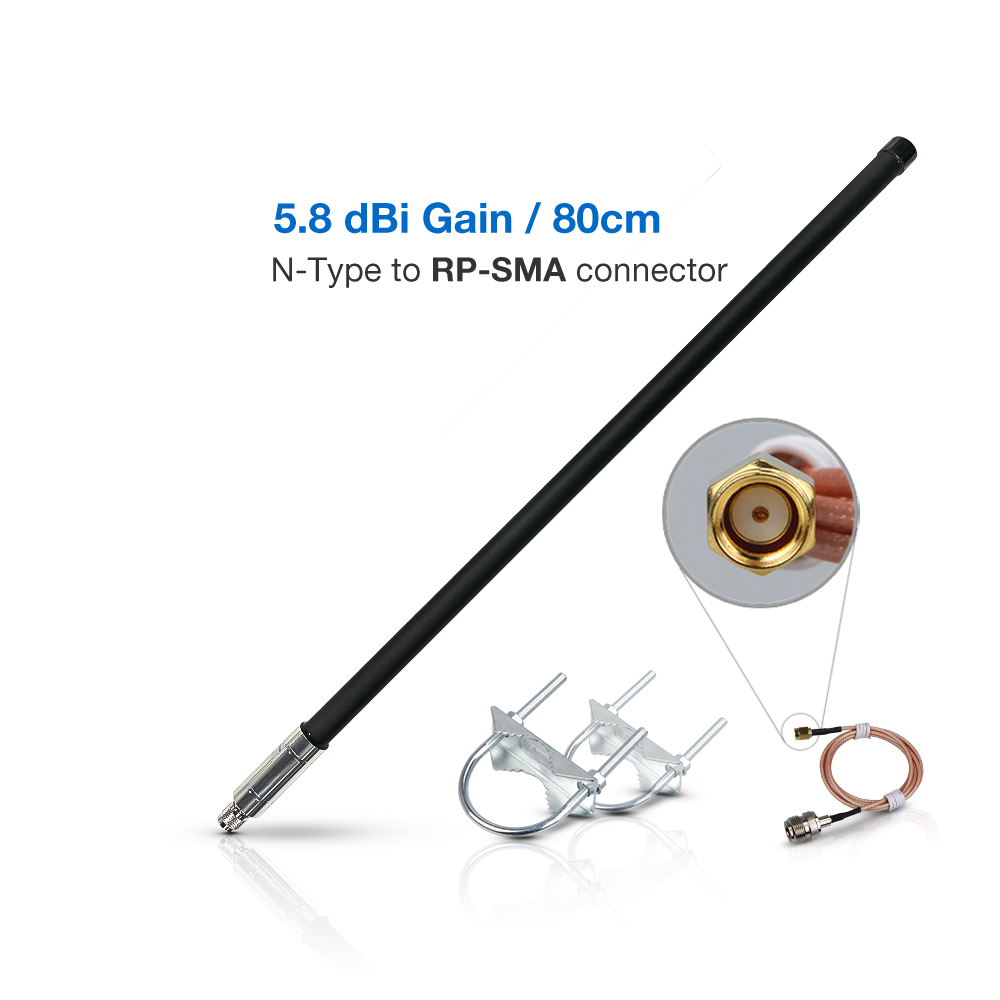
- Antenna Gain: Antenna gain, measured in dBi, reflects the directionality of the signal rather than its amplification. Higher gain antennas have stronger directionality and narrower beam angles, making them suitable for long-distance communication.
Is a High-Gain Antenna Advantageous?
Often, manufacturers of antennas (whether Wi-Fi, GPS, or TV antennas) specify the antenna gain, marketing high-gain antennas as superior and more expensive than their low-gain counterparts. The question is: do we want high gain?
The answer is that it depends. If you know exactly where your desired signal is coming from, you would want maximum gain in that direction. However, if the signal's direction is uncertain, a low-gain antenna is preferable. Here are a few examples to illustrate this:
Example #1 – TV Antennas: If you mount a TV antenna on your roof and know the broadcast antennas are to the south (for example, on a hill south of the city), then a high-gain antenna is preferred. Antennas with a gain of at least 12-15 dBi are ideal in such scenarios.
Example #2 – GPS (Global Positioning System): GPS antennas for mobile devices are receive-only. The job of the GPS antenna is to triangulate your position by measuring the received signal from multiple GPS satellites, which are in different directions relative to the receiving antenna. For this case, a highly directional antenna would not be preferred.
Example #3 – Mobile Cellular Antennas: The cellular antenna on your smartphone communicates with a single cellular network tower. However, the cellular antenna can be held in any orientation and position relative to the network tower. Hence, for mobile devices, a low-gain antenna is preferred.
Antenna Options from RAKwireless
RAKwireless offers a variety of antennas to suit different needs. Here are some options:
IP67 Rated Antennas:
IP65 Rated Antennas:
Factors Influencing Coverage Range
- Gateway and Node Specifications: The transmission (TX) power and reception (RX) sensitivity of both the gateway and the node significantly impact the coverage range.
- Antenna Height: Mounting height is a critical factor. In our WisGate Edge Pro RAK7289 Coverage Range Test Report , we achieved an 11 km coverage range with the gateway antenna mounted at a height of approximately 100 m.
- Interference: Various types of interference, such as physical obstructions and electromagnetic interference, can affect signal quality and coverage.
Recommendations for Antenna Selection
We often recommend the 5.1 dBi Fiberglass Antenna (RAKARG19) due to its balance of gain and coverage capabilities. This antenna is versatile and suitable for a wide range of applications.
Using Multiple Different Antennas?
Some may wonder if it’s beneficial to use different antennas (let’s say both RAKARG12 and RAKARG15) on the same 16-channel gateway to cover different distances. The two LoRa antenna connectors on a gateway mean there are two LoRa concentrator modules inside (making the gateway 16 channels). They work on different channels at any given time, therefore, using two different antennas for this purpose is unnecessary.
Conclusion
Selecting the right antenna is essential for maximizing the performance of your LoRaWAN gateway. By understanding the specifications and factors influencing coverage, you can make a well-informed choice. Refer to detailed datasheets and test reports to guide your decision-making process.
Explore the range of antennas we offer and find the one that best suits your needs in the RAKwireless Store. For custom recommendations or technical support, feel free to reach out to us. You can also visit our custom antenna design service page.